Blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about trust, transparency, and data security. While public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the foundation of decentralized finance (DeFi), enterprise blockchains are specifically designed to meet the needs of businesses, providing more control, privacy, and scalability. Both forms of blockchain offer unique features, but they cater to different use cases and user requirements.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between public and enterprise blockchains:
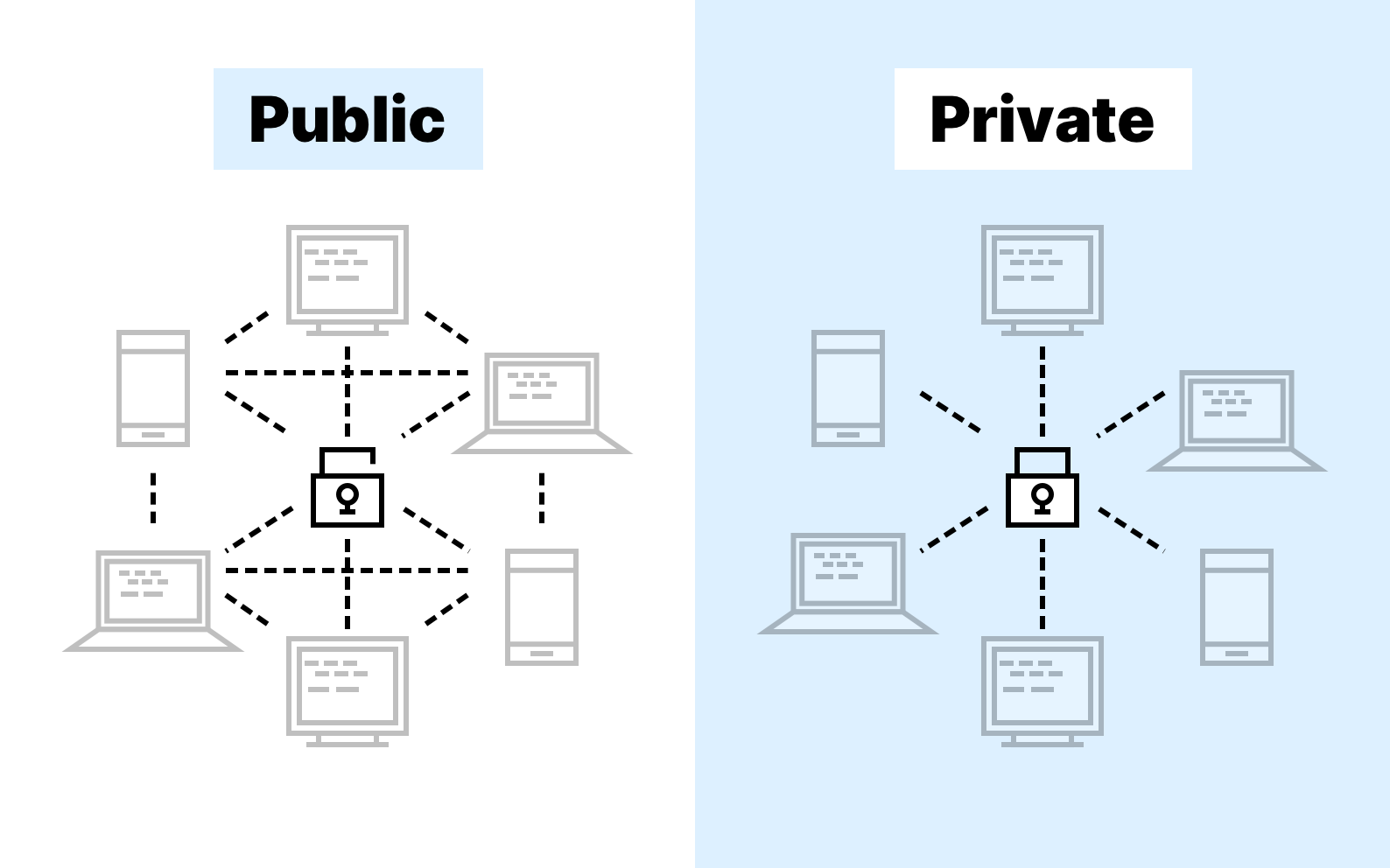
1. Accessibility and Permission
• Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains are open to anyone. Any individual or entity can join the network, participate in consensus processes, validate transactions, and maintain a copy of the ledger. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Polkadot.
• Enterprise Blockchain:
Enterprise blockchains, also known as permissioned blockchains, are designed for business use cases. Access to the network is restricted, and only authorized entities can participate. This ensures greater privacy, as data is only visible to those who have permission. Examples of enterprise blockchains include Hyperledger Fabric and Mandala Application Chain.
2. Consensus Mechanism
• Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains often use energy-intensive consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or newer models like Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions. These models are highly secure but can be slow and costly.
• Enterprise Blockchain:
Enterprise blockchains use private consensus mechanisms such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) or Raft Consensus Algorithm. These mechanisms are more energy-efficient and faster than PoW, allowing enterprise networks to achieve consensus quickly while maintaining security.
3. Scalability
• Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains often face scalability issues due to their decentralized and global nature. As more participants join the network, the system can become slower, and transaction fees may rise. While there are ongoing improvements in public blockchains, scalability remains a challenge.
• Enterprise Blockchain:
Enterprise blockchains are designed for high scalability. Because they are permissioned and involve fewer participants, transactions are processed faster, and the network can handle a higher throughput. This scalability is essential for businesses that require efficient and reliable systems.
4. Privacy
• Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains are transparent by nature. Every transaction is visible to everyone on the network, which is ideal for use cases where transparency is a key requirement, such as DeFi or voting systems.
• Enterprise Blockchain:
In enterprise blockchains, privacy is paramount. The data is only accessible to authorized participants. Businesses often have to handle sensitive information, and enterprise blockchains provide the necessary privacy controls to ensure that critical business data is not exposed.
5. Use Cases
• Public Blockchain:
Public blockchains are ideal for applications that require decentralization and transparency. Common use cases include cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, and voting systems.
• Enterprise Blockchain:
Enterprise blockchains are built for specific business needs. They are commonly used in industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, financial services, and government for applications that require controlled access, privacy, and efficiency.
Top 5 Enterprise Blockchains in the Market
Here are the top enterprise blockchain platforms that are transforming how businesses operate:
1. Mandala Application Chain
• Overview: Developed by Baliola, Mandala Application Chain is a blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) platform specifically designed for enterprise use. It offers businesses the ability to build their own blockchain networks with high scalability, privacy, and security. Mandala focuses on industries such as carbon markets, digital identity, and supply chain management, enabling businesses to leverage blockchain’s power without needing to manage complex infrastructure.
• Key Features:
• Permissioned Blockchain with customizable access control.
• High Scalability for enterprise applications.
• Blockchain-as-a-Service model, reducing setup and maintenance costs.
2. Hyperledger Fabric
• Overview: Hyperledger Fabric is one of the most well-known enterprise blockchain frameworks, hosted by the Linux Foundation. It’s modular and highly flexible, allowing businesses to configure it to suit various use cases across industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain.
• Key Features:
• Modular architecture, allowing businesses to plug in components like consensus algorithms.
• Permissioned network with advanced identity management.
• Highly customizable for enterprise needs.
3. R3 Corda
• Overview: R3’s Corda is a blockchain platform specifically designed for the financial sector but has since expanded into other industries. Corda enables businesses to build interoperable blockchain networks where they can share data securely and efficiently without compromising privacy.
• Key Features:
• Strong focus on data privacy and selective data sharing.
• Custom-built for regulatory environments, ensuring compliance with local laws.
• Interoperability with existing systems and other blockchain networks.
4. Quorum (Consensys Quorum)
• Overview: Quorum is an enterprise-focused version of the Ethereum blockchain. Originally developed by JP Morgan, it is now managed by Consensys. Quorum allows businesses to run private blockchains with the benefits of Ethereum’s robust architecture, offering smart contract functionality tailored for business needs.
• Key Features:
• Built on Ethereum, providing compatibility with Ethereum smart contracts.
• Focus on privacy and transaction confidentiality.
• Permissioned blockchain ideal for financial and supply chain use cases.
5. IBM Blockchain
• Overview: IBM Blockchain is built on Hyperledger Fabric and offers a Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) solution. IBM’s blockchain services are used by businesses to build and scale networks that require trust, transparency, and efficiency. Key industries include food traceability, supply chain management, and financial services.
• Key Features:
• Enterprise-grade security and privacy.
• Modular services for customizing blockchain networks.
• Scalable and highly reliable infrastructure.
Conclusion
Both public and enterprise blockchains have their own strengths and use cases. While public blockchains offer decentralization and transparency ideal for cryptocurrencies and DeFi applications, enterprise blockchains are built for privacy, efficiency, and scalability—key requirements for industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
As blockchain adoption continues to grow, platforms like Mandala Application Chain and other leading enterprise blockchains are set to play a crucial role in transforming how businesses operate, ensuring that companies can leverage the benefits of blockchain while maintaining the control and security they need.
Stay Updated: Follow Baliola for more insights on how Mandala Application Chain is empowering businesses with blockchain technology